Table of Contents
ToggleMastering the Incident Lifecycle Stages: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In the fast-changing digital landscape, strong cybersecurity is crucial for organisations worldwide. Effectively managing & responding to incidents is vital to protect sensitive data, ensure business continuity & maintain trust with customers & stakeholders. This Journal will guide you through the Incident Lifecycle Stages, empowering effective Incident Management, understanding each stage from identification to recovery, ensuring confidence in handling incidents.
The surge in cyberattacks & data breaches emphasises the urgency for organisations to take a proactive stance on cybersecurity. Incident management, a key component of a robust cybersecurity strategy, entails the systematic identification, analysis & response to security incidents. Whether facing malware intrusions, Distributed Denial-of-Service [DDoS] attacks, phishing attempts or other breaches, a well-defined Incident Management Process significantly reduces potential damages & speeds up recovery.
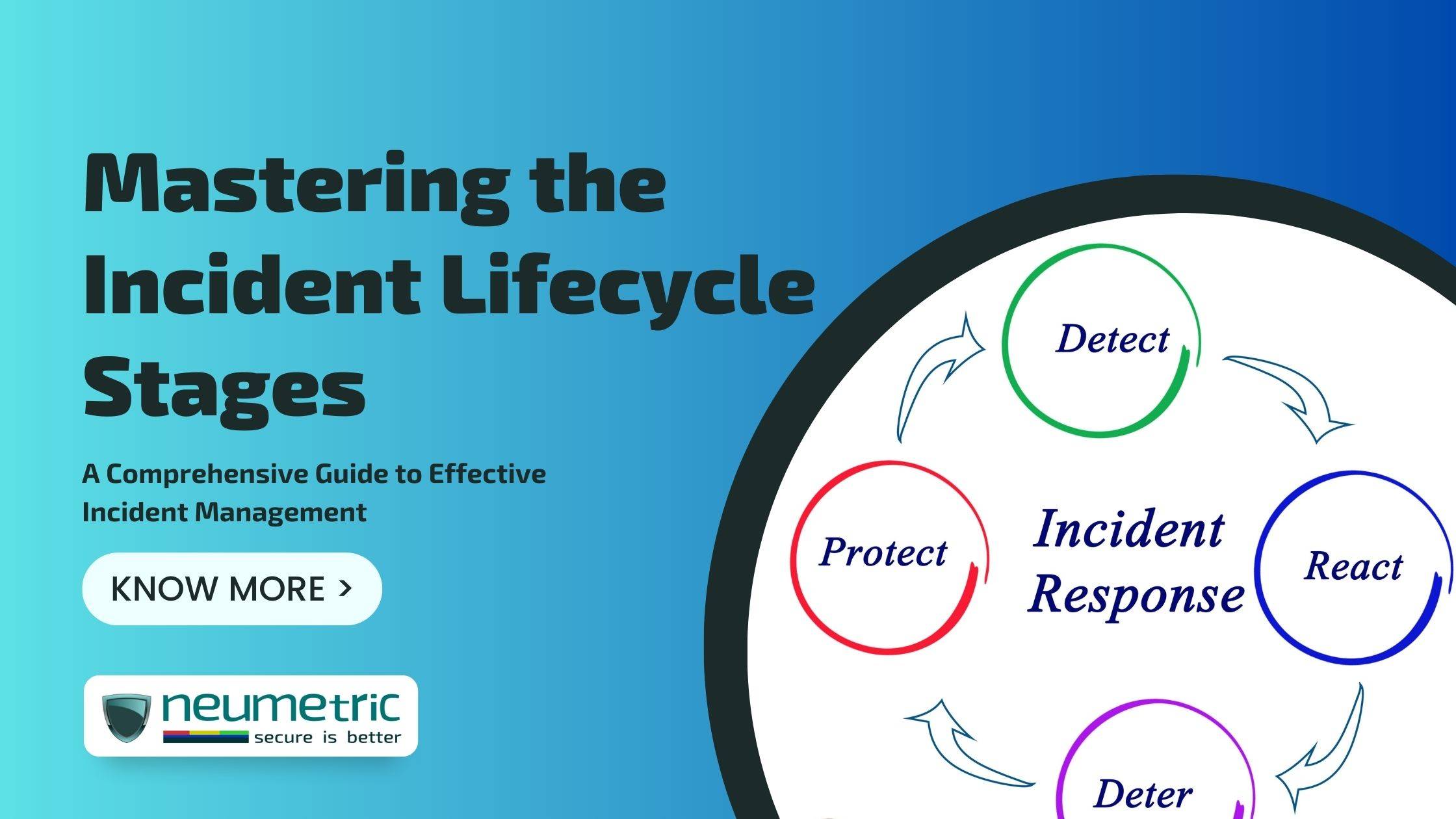
Incident Lifecycle Overview
The Incident Lifecycle provides a clear roadmap for addressing security breaches & cyber incidents. With key stages, it outlines a systematic approach to detect, mitigate & recover from breaches effectively. Each stage is vital for incident management, ensuring swift resolution while minimising damages.
Comprehending each Incident Lifecycle stage is vital for an effective response strategy. Understanding incident identification, containment, eradication & recovery enables prompt & decisive action by cybersecurity professionals & IT teams. This knowledge allows targeted best practices, precise incident handling & continuous improvement of incident management processes based on real-world experience & lessons learned.
Common models customised to meet organisational & industry demands include National Institute of Standards and Technology [NIST] Incident Response Lifecycle, Systems Administration and Network Security [SANS] Incident Handling Process & Information Technology Infrastructure Library [ITIL] Service Lifecycle. Exploring these frameworks enhances incident response efficiency, aligning with unique structures & compliance objectives. Adopting a well-established Incident Lifecycle model strengthens cybersecurity posture, safeguards vital assets & streamlines incident management efforts.
Stage 1: Incident Identification & Reporting
The Incident Identification & Reporting stage is the critical first step in the lifecycle. Swiftly detecting & confirming security incidents is the primary focus. Key objectives include identifying the incident’s nature, scope & potential impact, enabling immediate actions to mitigate further harm. Cybersecurity teams & monitoring systems diligently observe network activities & employ intrusion detection tools, laying the foundation for an effective Incident Response Process.
Organisations employ advanced tools like Intrusion Detection System [IDS], Intrusion Prevention System [IPS], Security Information & Event Management [SIEM] systems, threat intelligence feeds & anomaly detection algorithms to promptly detect incidents. These tools actively monitor network traffic, correlate events & identify potential threats, enabling swift incident response & preventing major security breaches.
Efficient incident reporting & documentation are vital in the Identification & Reporting stage. Prompt communication ensures timely reporting to the response team. Detailed documentation, including detection time & involved assets, aids post-incident analysis & meets regulatory requirements. Well-defined strategies create accurate incident logs, easing the transition to subsequent stages.
Stage 2: Incident Triage & Classification
In Stage 2 of the Incident Lifecycle, Incident Triage & Classification play a key role. Incident triage swiftly assesses & prioritises incoming incidents, allocating resources effectively to address the most critical threats first. The main objectives are to minimise response time, prevent further damage & prioritise incidents based on severity & potential impact. Triage acts as a crucial filter, separating high-priority incidents needing immediate attention, streamlining the response process & improving overall efficiency.
Effectively prioritising incidents is crucial for efficient incident response. Techniques like severity & impact metrics are used to assess the potential damage to critical assets or services. Considering factors such as data exposure, compliance violations & reputational damage also helps establish incident priority. Collaborative efforts among security analysts, incident response teams & stakeholders contribute to a comprehensive understanding of each incident’s significance & impact.
Organisations can adopt categorization frameworks for consistent & standardised incident classification. These frameworks, like Common Vulnerability Scoring System [CVSS] for vulnerability severity scoring & Traffic Light Protocol [TLP] for dissemination restrictions, structure incidents based on nature, origin & potential impact. Such implementation helps incident responders understand unique incident characteristics, enabling precise categorization & focused response efforts for each incident type.
Stage 3: Incident Investigation & Analysis
Stage 3, Incident Investigation & Analysis, is crucial in the Incident Response Process. This systematic examination uncovers key details, such as attack vectors, affected systems & potential data breaches. Valuable insights gained from thorough investigation inform targeted approaches for containment, eradication & recovery. Additionally, identifying patterns & trends enhances cybersecurity strategies & preemptive measures against future threats.
During investigation & analysis, responders gather evidence & conduct digital forensics, vital for legal purposes & prosecuting attackers. Digital assets, like log files & malware samples, are examined systematically to reconstruct the attack timeline & identify techniques used. Advanced forensics tools trace origins, pinpoint entry points & gauge unauthorised access, forming a strong evidence-driven incident response plan to enhance future defences.
In the investigation & analysis stage, identifying the incident’s root cause & impact is vital. Root cause analysis uncovers vulnerabilities or weaknesses in systems or processes, aiding effective corrective actions to prevent recurrence. Assessing the incident’s impact helps gauge data loss & operational disruptions, enabling informed decision-making, cybersecurity reinforcement & risk mitigation in the future.
Stage 4: Incident Containment & Eradication
In Stage 4 of the Incident Lifecycle, Containment & Eradication strategies aim to halt the incident’s spread & prevent further damage. Isolating affected systems & suspending user privileges limit the impact, while firewall rules & access controls restrict unauthorised access. Responders also focus on mitigating active threats by patching software, updating security configurations & enhancing system hardening to prevent future incidents.
In this stage, responders remove the threat & restore affected systems. Using knowledge from the investigation, they meticulously eliminate malware, malicious code or unauthorised access points. Specialised antivirus & anti-malware tools aid in detection & removal. Restoring systems to pre-incident states relies on robust backup & recovery procedures. Precision in these techniques minimises downtime & ensures a swift return to normal operations.
Seamless collaboration between incident responders, IT teams & security professionals is vital for successful containment & eradication. Close communication allows effective execution of containment strategies without disrupting critical business operations. Responders & IT teams isolate affected systems, implement firewall rules & enforce access controls while security teams offer ongoing threat intelligence & support to adapt to evolving threats. This synergy ensures swift & efficient incident eradication, reducing damages & fortifying the organisation’s cybersecurity posture.
Stage 5: Incident Recovery & Remediation
Stage 5 of the Incident Lifecycle, Incident Recovery & Remediation, prioritises restoring normalcy swiftly. This phase addresses vulnerabilities, weaknesses & damages caused by the incident to minimise downtime, financial losses & maintain customer trust. Effective communication with stakeholders reassures them during the recovery process. Swift recovery ensures continuity, essential services resumption & system control regained.
The Incident Recovery & Remediation stage aims to restore data, systems & services to their pre-incident state. This involves systematic data recovery from backups, ensuring integrity & validating the process. Rebuilding or reconfiguring compromised systems may be necessary, followed by rigorous testing to ensure proper functioning. Thorough documentation is crucial for post-incident analysis & future incident response plan improvements.
In addition to recovery, the Incident Recovery & Remediation stage enhances the security posture. Insights from investigation guide improvements, addressing vulnerabilities in systems & security controls. Implementing enhancements involves patching, updating configurations & strengthening access controls. Training & awareness programs reinforce cybersecurity best practices. Proactive security measures defend against future incidents, reducing likelihood & impact of cyber threats.
Stage 6: Incident Post-Mortem & Lessons Learned
Stage 6 of the Incident Lifecycle, Incident Post-Mortem & Lessons Learned, is critical for incident response. After resolving the incident, a thorough review analyses the entire response process to gain insights, assess procedures & identify shortcomings. Comprehensive post-incident reviews offer valuable knowledge to enhance overall cybersecurity posture.
In the post-mortem phase, incident response teams closely examine handling, communication, decision-making & collaboration. Identifying areas for improvement & lessons learned fine-tunes response plans & protocols. Pinpointing bottlenecks streamlines workflows & optimises resource allocation for enhanced efficiency. Addressing knowledge gaps prioritises cybersecurity team training & development for continuous improvement & readiness for future incidents.
The post-mortem review knowledge updates incident response plans & security measures. Incorporating lessons learned & best practices builds a more robust & agile response framework. Adjusting plans for emerging threats & addressing weaknesses ensures a cohesive response. Updates in the cybersecurity strategy proactively address vulnerabilities & prevent future incidents. Continuous improvement based on lessons learned keeps organisations ahead in the battle against cyber threats.
Integration of Incident Lifecycle Stages with Incident Response Platforms
Incorporating Incident Response Platforms into the lifecycle brings streamlined & efficient incident management to organisations. These platforms centralise incident handling from detection to resolution, automating tasks for faster response times & threat containment. Real-time communication & collaboration among responders enhance incident handling during high-stress scenarios. Additionally, platforms offer comprehensive reporting & analytics, providing valuable insights into incident trends & response strategy effectiveness, improving cybersecurity posture continuously.
When selecting an incident response platform, essential features should be considered for seamless integration with the lifecycle stages. Automated incident ticketing & tracking enable structured logging of incident details & updates. Integration with threat intelligence feeds allows real-time threat detection & data enrichment. Robust case management functionalities ensure easy collaboration, documentation & evidence preservation. Built-in analytics & reporting tools monitor incident metrics, measure response performance & generate comprehensive reports for stakeholders & compliance.
Various incident response platforms are available, catering to organisations of different sizes & industries. Some platforms seamlessly integrate with the Incident Lifecycle, offering a user-friendly interface for managing incidents from discovery to resolution. It enables real-time collaboration during investigation & containment. On the other hand, some other platforms feature advanced automation for rapid response & customizable reporting for data-driven decisions. Carefully selecting the right platform optimises incident management efforts & enhances response to evolving threats.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering the Incident Lifecycle Stages is vital for a secure digital environment. We explored various phases, from identification & investigation to containment, eradication & recovery. Each stage is crucial in swiftly addressing security breaches & bolstering cybersecurity posture, safeguarding critical assets & sensitive data.
Adopting a systematic incident management approach is crucial. Incidents are unpredictable & can severely disrupt an organisation’s operations, finances & reputation. A clear response plan ensures teams are prepared to respond efficiently, reducing response times, limiting incident spread & mitigating its impact. This approach fosters continuous learning, enabling organisations to strengthen future incident response capabilities by applying lessons from past incidents.
As we conclude, we encourage organisations to implement best practices for effective incident response & mitigation. Regular training & simulations familiarise teams with the process, enabling swift & confident responses. Fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness among employees enhances detection capabilities & reduces successful attacks. Staying informed about cybersecurity threats allows proactive adjustment of response strategies to counter emerging risks. Strengthening incident response capabilities is a continuous journey, ensuring asset protection & a safer digital future.
FAQs
What are the 5 stages of the Incident Lifecycle?
The five stages of the Incident Lifecycle are:
1. Incident Identification & Reporting – Detecting & reporting potential security incidents.
2. Incident Triage & Prioritization – Assessing the severity & impact of incidents to prioritise response efforts.
3. Incident Containment & Eradication – Taking immediate actions to contain the incident & remove threats.
4. Incident Recovery – Restoring affected systems & data to normal operation.
5. Incident Post-Mortem & Lessons Learned – Analysing the incident to understand its root cause & identify improvements for future incident response.
What are the 4 stages of an incident?
The four stages of an incident are typically referred to as the “Four Rs”:
1. Recognition – Identifying the incident or security breach.
2. Response – Taking immediate actions to contain & mitigate the incident.
3. Recovery – Restoring systems & services to normal operation.
4. Review – Analysing the incident & the organisation’s response to prevent similar incidents in the future & improve incident handling procedures.