Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
The General Data Protection Regulation [GDPR] is a comprehensive data protection law that came into effect on Fri, 25-May-2018, in the European Union [EU] & the European Economic Area [EEA]. It sets strict requirements for organisations handling personal data & aims to enhance individual’s rights & control over their data in the digital age. GDPR applies to all organisations, regardless of their location, if they handle the personal data of individuals residing in the EU. Compliance with GDPR is not only a legal obligation but also crucial for maintaining customer trust & protecting individual’s privacy.
Complying with GDPR is of utmost importance for organisations in today’s data-driven world. With the increasing frequency of data breaches & privacy concerns, adhering to the regulations helps organisations establish a strong foundation for data protection & security. Non-compliance can lead to severe financial penalties & reputational damage. By complying with GDPR, organisations demonstrate their commitment to respecting individual’s rights & safeguarding their personal data, thereby fostering trust & credibility with customers & stakeholders.
This Journal aims to provide guidance on effective GDPR compliance. We break down key principles, outline steps for compliance, address specific areas, discuss challenges & offer best practices. Our goal is to empower organisations with knowledge & tools to prioritise data protection, maintain compliance & foster a culture of privacy & trust.
Understanding the Key Principles of GDPR
GDPR is built upon several fundamental principles that organisations must adhere to when processing personal data. Let’s dive deeper into each principle:
- Lawful basis for data processing: Organisations must have a valid legal basis for processing personal data. This includes obtaining consent, fulfilling contractual obligations, complying with legal requirements, protecting vital interests, performing a public task or pursuing legitimate interests.
- Data minimization & purpose limitation: GDPR emphasises collecting only the necessary personal data for a specific purpose & using it only for that purpose. Organisations should avoid excessive data collection & ensure data is not retained longer than necessary.
- Individual rights & consent: GDPR grants individuals various rights regarding their personal data. These rights include the right to access their data, rectify inaccuracies, erase data under certain circumstances, restrict processing, object to processing & obtain portable copies of their data. Consent should be obtained in a clear, transparent manner & individuals should have the freedom to withdraw consent at any time.
- Data security & breach notification: Organisations must implement appropriate technical & organisational measures to ensure the security of personal data. This includes measures such as encryption, access controls, regular security audits & employee training. In case of a data breach, organisations must promptly notify the relevant supervisory authority and, in certain cases, the affected individuals.
- Accountability & data protection officers: GDPR places an emphasis on accountability, requiring organisations to demonstrate compliance with the regulation. Some organisations may be required to appoint a Data Protection Officer [DPO] who acts as an independent expert responsible for overseeing data protection activities & acting as a point of contact for individuals & regulatory authorities.
Steps to Achieve GDPR Compliance
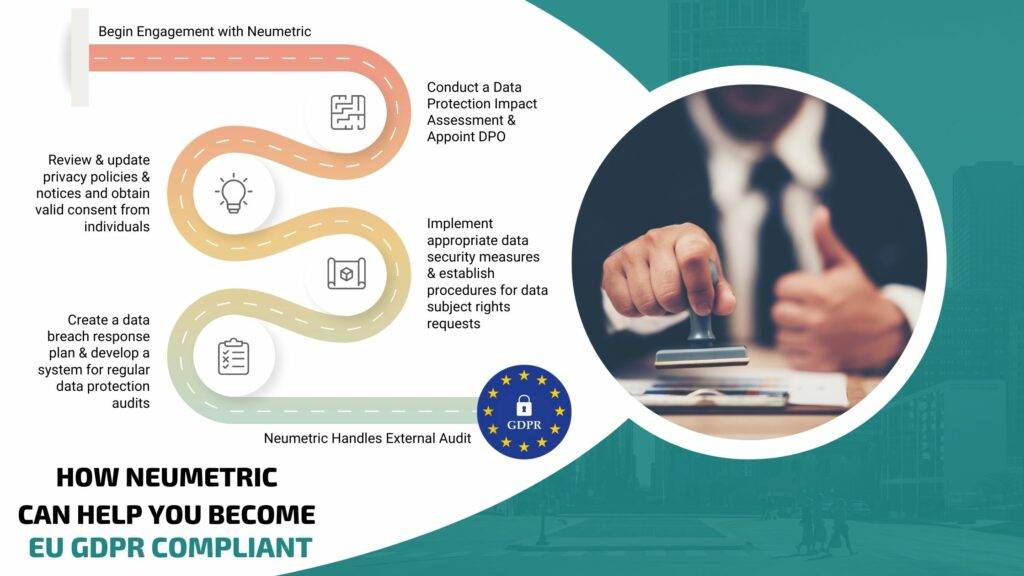
To achieve GDPR compliance, organisations should take the following steps:
- Conduct a Data Protection Impact Assessment [DPIA]: A DPIA helps organisations identify & assess the potential risks to an individual’s privacy when processing personal data. It enables organisations to evaluate the necessity, proportionality & mitigation measures related to data processing activities.
- Appoint a Data Protection Officer [DPO] if required: Certain organisations, based on the nature & scale of their data processing activities, are mandated to appoint a DPO. The DPO plays a crucial role in advising on data protection matters, monitoring compliance & acting as a point of contact for individuals & regulatory authorities.
- Review & update privacy policies & notices: Privacy policies & notices should be transparent, easily understandable & readily accessible. They should inform individuals about the types of personal data collected, the purposes of processing, the lawful basis for processing, data retention periods & the rights individuals have regarding their data.
- Obtain valid consent from individuals: When relying on consent as a legal basis for processing personal data, organisations must ensure that the consent obtained is freely given, specific, informed & unambiguous. Clear mechanisms for obtaining & withdrawing consent should be provided.
- Implement appropriate data security measures: GDPR mandates the implementation of appropriate technical & organisational measures to ensure the security & confidentiality of personal data. These measures may include encryption, pseudonymization, access controls, regular security assessments & employee training on data protection.
- Establish procedures for data subject rights requests: Organisations should have well-defined processes in place to handle data subject rights requests promptly & efficiently. This includes providing individuals with access to their data, rectifying inaccuracies, erasing data when requested & ensuring data portability.
- Create a data breach response plan: Organisations should develop a comprehensive plan to address potential data breaches. The plan should include steps for identifying & containing breaches, investigating their impact, notifying the relevant supervisory authority & affected individuals & implementing remedial measures to prevent similar incidents in the future.
- Develop a system for regular data protection audits: Regular audits & assessments help organisations identify areas of non-compliance, evaluate the effectiveness of data protection measures & implement necessary improvements. Audits also demonstrate a commitment to ongoing compliance with EU GDPR.
Click here to check out Neumetric’s EU GDPR Compliance Checklist Guide for 2024.
Ensuring Compliance in Specific Areas
Compliance with GDPR extends to specific areas that require additional attention:
- Processing personal data of children: When processing personal data of children, organisations must implement additional safeguards to ensure their privacy & protection. This includes obtaining verifiable parental consent, using age-appropriate language in privacy notices & providing clear information about data processing activities.
- Transferring data outside the European Economic Area [EEA]: Transferring personal data to countries outside the EEA requires organisations to ensure an adequate level of protection for the data. This can be achieved through measures such as relying on an adequacy decision by the European Commission, implementing appropriate safeguards [e.g. Standard Contractual Clauses] or relying on derogations provided by GDPR.
- Navigating the requirements for data processors & controllers: GDPR distinguishes between data processors & data controllers, each having specific obligations. Organisations should clearly define roles & responsibilities when engaging third-party processors, ensuring compliance through robust contractual agreements & ongoing monitoring.
- Handling sensitive personal data & special categories of data: GDPR imposes stricter requirements for processing sensitive personal data, such as health information or biometric data. Organisations must ensure they have a valid legal basis for processing such data & implement additional safeguards to protect individual’s rights & privacy.
- Addressing the right to be forgotten & data retention policies: GDPR recognizes individual’s right to request the erasure of their personal data under certain circumstances. Organisations should have clear policies & procedures in place to handle such requests & ensure data is retained only for the necessary & lawful periods.
Compliance Challenges & Best Practices
Organisations often face challenges such as lack of awareness about GDPR requirements, limited resources for implementing necessary measures, complexity in adapting existing systems & processes & keeping up with evolving regulatory guidance. Identifying & addressing these challenges proactively is key to successful compliance.
Organisations can adopt several best practices to effectively manage & protect personal data. These include implementing privacy by design principles, conducting regular staff training & awareness programs on data protection, regularly reviewing & updating data protection practices & procedures, maintaining proper documentation of data processing activities & establishing a culture of privacy & data protection within the organisation.
Achieving GDPR compliance is not a one-time effort but an ongoing process. Organisations should establish a comprehensive compliance program that includes regular assessments of data protection practices, continuous monitoring of regulatory changes & updates, periodic reviews of policies & procedures & ongoing staff education & awareness initiatives.
GDPR is a dynamic regulation that may undergo updates & changes over time. Organisations should stay informed about regulatory developments, seek guidance from relevant supervisory authorities & adjust their practices accordingly to ensure ongoing compliance.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
If an organisation fails to comply with GDPR, it will result in a fine ranging from 10 Million Euros to four (4) percent of the company’s annual global turnover. Fines & penalties depend on the severity of the breach. It also depends on whether the company is deemed to have taken compliance & regulations around security in a serious enough manner.
A maximum fine of 20 Million Euros or four (4) percent of worldwide turnover, whichever is greater, is for breaches of the rights of the data subjects, failure to put procedures in place & unauthorised international transfer of personal data.
A lower fine of 10 Million Euros or two (2) percent of worldwide turnover is applied to companies that mishandle data in other ways. For instance, failure to build in privacy by design, ensuring data protection is applied in the first stage of a project, failure to report a data breach & be compliant by appointing a data protection officer.
GDPR breaches can have significant reputational consequences. Organisations risk losing customer trust, damaging their brand image & facing negative impacts on customer relationships & business operations. Non-compliance with GDPR may expose organisations to legal actions. Affected individuals can seek damages for material or non-material harm resulting from violations of their rights. Additionally, supervisory authorities have the power to take enforcement actions, including issuing warnings, reprimands & orders to rectify non-compliance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, compliance with the General Data Protection Regulation [GDPR] is essential for organisations handling personal data. By adhering to key principles, implementing necessary steps & adopting best practices, organisations prioritise data protection & privacy, meeting legal obligations & safeguarding customer trust. Steps include lawful data processing, minimising & defining data usage, respecting individual rights, ensuring data security & being accountable. Compliance areas include processing data of children, data transfers outside the EEA, data processors & controllers, sensitive data handling & data retention policies.
Overcoming challenges, such as awareness, resources, system adaptation & staying updated, is crucial. Ongoing compliance programs, best practices adoption & vigilance towards regulatory changes are vital. Non-compliance can result in severe penalties, reputational damage & legal actions. Prioritising data protection & privacy is an ethical responsibility. Proactive steps towards GDPR compliance demonstrate commitment to respecting rights & maintaining trust. Compliance ensures a secure & trustworthy environment for personal data.
FAQs
How can I comply with data protection?
To comply with data protection, you can follow key steps such as understanding relevant data protection laws & regulations, implementing appropriate security measures, obtaining valid consent, minimising data collection, honouring individual’s rights & regularly reviewing & updating your privacy practices.
To comply with data protection in the context of GDPR, organisations should follow key steps, such as conducting a Data Protection Impact Assessment, appointing a Data Protection Officer if required, reviewing & updating privacy policies, obtaining valid consent, implementing data security measures, establishing procedures for data subject rights requests & creating a data breach response plan.
Click here to learn more about how to become compliant with GDPR by following the right steps!
Who has to comply with data protection regulations?
All organisations that handle personal data, regardless of their location, have to comply with data protection regulations. These regulations apply to both data controllers (organisations that determine the purposes & means of processing) & data processors (organisations that process data on behalf of data controllers).
GDPR applies to all organisations, regardless of their location, if they handle the personal data of individuals residing in the European Union [EU]. It is not limited to EU-based organisations. Neumetric’s Journal titled Who Needs to Comply with GDPR provides a greater understanding of who needs to comply with the EU GDPR Regulation.
Why do we need to comply with data protection?
Compliance with data protection is necessary to protect an individual’s privacy, maintain trust & ensure the security of personal data. It helps organisations adhere to legal obligations, prevent data breaches, mitigate financial & reputational risks & foster a culture of privacy & data security.
What are the 3 rules of Data Protection Act?
The three (3) rules of Data Protection Act are:
- Data must be processed fairly & lawfully.
- Data must be used for specified purposes & not further processed in a way that is incompatible with those purposes.
- Data must be kept secure & protected against unauthorised access, loss, or destruction.
What are the common challenges in achieving GDPR compliance?
Common challenges in achieving GDPR compliance include lack of awareness about requirements, limited resources, complexity in adapting existing systems & keeping up with evolving regulatory guidance. Identifying & addressing these challenges proactively is crucial.





